代码解构

Baseline代码解构
数据读取及预处理
我个人觉得这里的数据处理是比较精妙的,可以把同样的思想应用到RGB输入里
数据准备:
- 得到从群体类别到id的映射
- 群体行为类别权重
- 个体行为类别权重
- 所有的个体行为类别标签
- 所有群体行为标签
- 所有个体行为标签
- 所有的clip的关键点数据的文件路径
- 所有的(video,clip)元组
- 球轨迹
- 边界框
步骤:
- store the dict {(video,clip) : group action id} in
annotations_thisdatasetdir - store all the current split’s joint data paths in
clip_joints_path - get current split’s video, clip into
clips - get correspond group labels in
annotations - get correspond person labels in
person_actions_all - count the number of clips
数据增强:
- 保存一个副本作为真实数据,每次用真实数据去增强数据集
1 | # 只有训练才需要进行增强 |
- 设置随机数
1 | if self.args.horizontal_flip_augment and self.split == 'train': |
数据分析:
- 我们需要对关键点数据进行统计分析。如果没有统计结果文件的话,我们需要得到以下信息:
1 | joint_xcoords = [] |
注意,这里统计分析的步骤需要包含增强数据
对于每一个clip joint,我们先将它读到 joint_raw
- 其次我们需要采样T帧:
1 | frames = sorted(joint_raw.keys())[self.args.frame_start_idx:self.args.frame_end_idx+1:self.args.frame_sampling] |
- 如果存在数据增强的话,如果需要有扰动,需要提前初始化
1 | if self.args.horizontal_flip_augment: |
- 还有个比较特殊的dropout增强:这里仅需设置随机性即可
1 | # To compute statistics, no need to consider the random agent dropout augmentation, |
- 因为姿态估计是存在错误的,所以需要对不合理的进行修改:
1 | joints_sanity_fix() # 函数 |
- 之后就可以去更新上面的坐标了:
1 | # 更新joints list |
- 有了上面这些,我们就可以去计算平均值和标准差了:
1 | joint_xcoords_mean, joint_xcoords_std = np.mean(joint_xcoords), np.std(joint_xcoords) |
- 计算完成后需要保存统计数据:
1 | # 保存统计数据 |
- 如果有扰动的话还需要保存下来:
1 | if self.args.horizontal_flip_augment and self.args.horizontal_flip_augment_purturb: |
数据获取:
- 得到person_labels:
1 | person_labels = torch.LongTensor(person_labels[frames[0]].squeeze()) |
- 使用数据增强:
1 | # if vertical move augmentation and is training |
- 并进行合法性检查
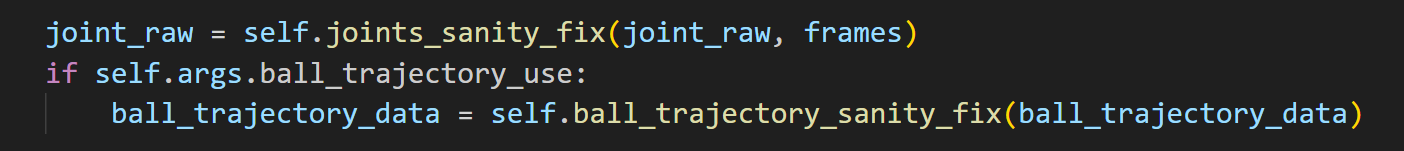
- 获得4种类型的joint features并将它们进行连接:
1 | joint_feats = torch.cat((torch.Tensor(np.array(joint_feats_basic)), |
- joint_coords_all 目的是为了图像坐标嵌入
1 | joint_coords_all = [] # (N, J, T, 2) |
- joint_feats_basic 对关键点坐标进行标准化
1 | joint_feats_basic = [] # (N, J, T, d_0_v1) |
joint_feats_advanced 对关键点信息进归一化
joint_feats_metrics
接下来,如果当前正在训练,并且使用dropout增强的话:
1 | # if random agent dropout augmentation and is training |
- 最后,返回数据
1 | return joint_feats, label, video, clip, person_labels#, ball_feats |
模型处理模块
- 获得所有需要的维度信息
1 | B = joint_feats_thisbatch.size(0) |
- 首先进行图像坐标位置编码
1 | # image coords positional encoding |
- 其次进行时间位置编码
1 | # time positional encoding |
- 再进行关键点类型嵌入编码
1 | # joint classes embedding learning as tokens/nodes |
- 最后将这些进行拼接得到编码后的关键点信息
1 | joint_feats_composite_encoded = torch.cat( |
- 之后进行投影:注意,这里时间维度已经没有了
1 | # PROJECTIONS |
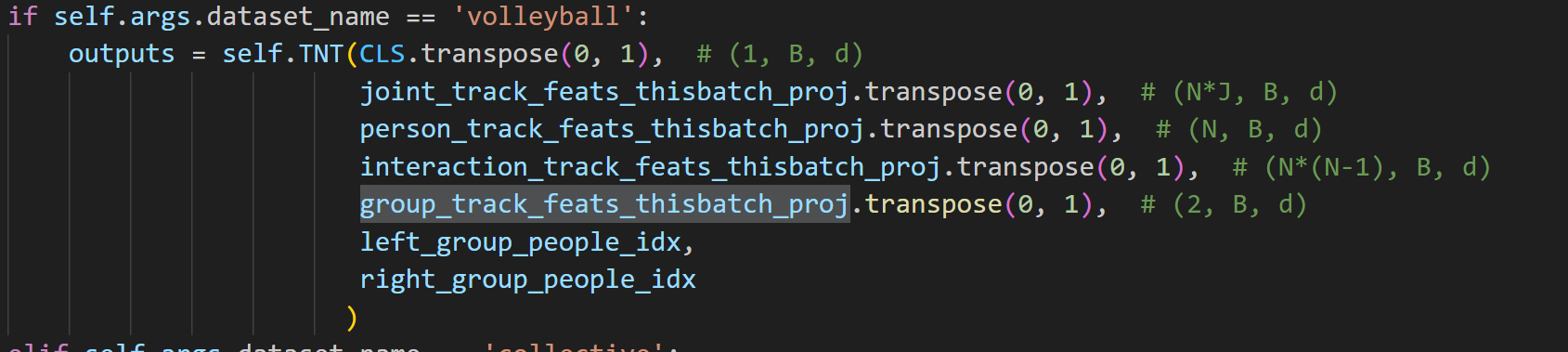
- 这里还有两个track, interaction track & group track,思想是类似的
- 接下来将各个track输入到TNT网络中进行处理:
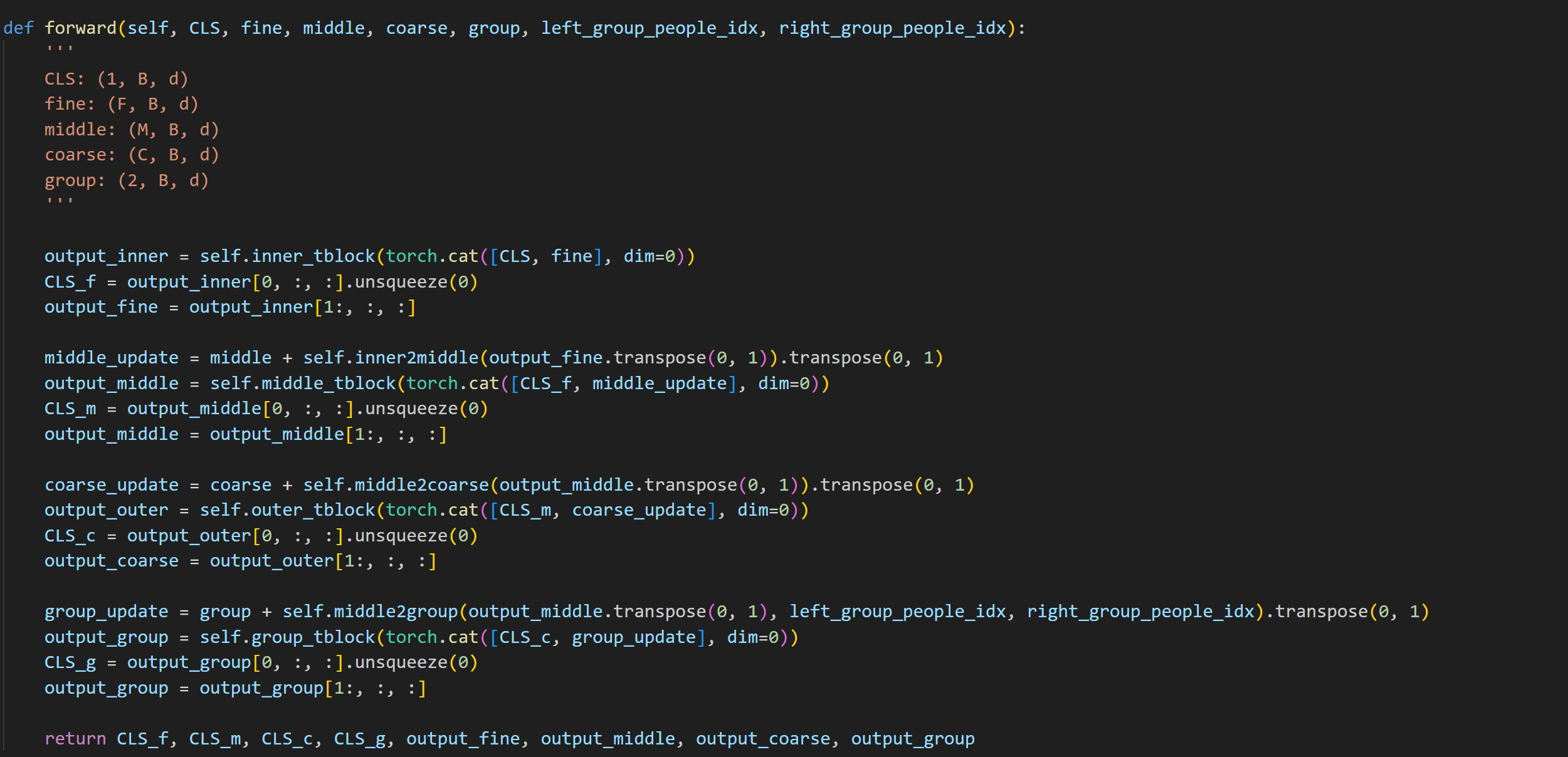
- TNT的主干是TNT_block:
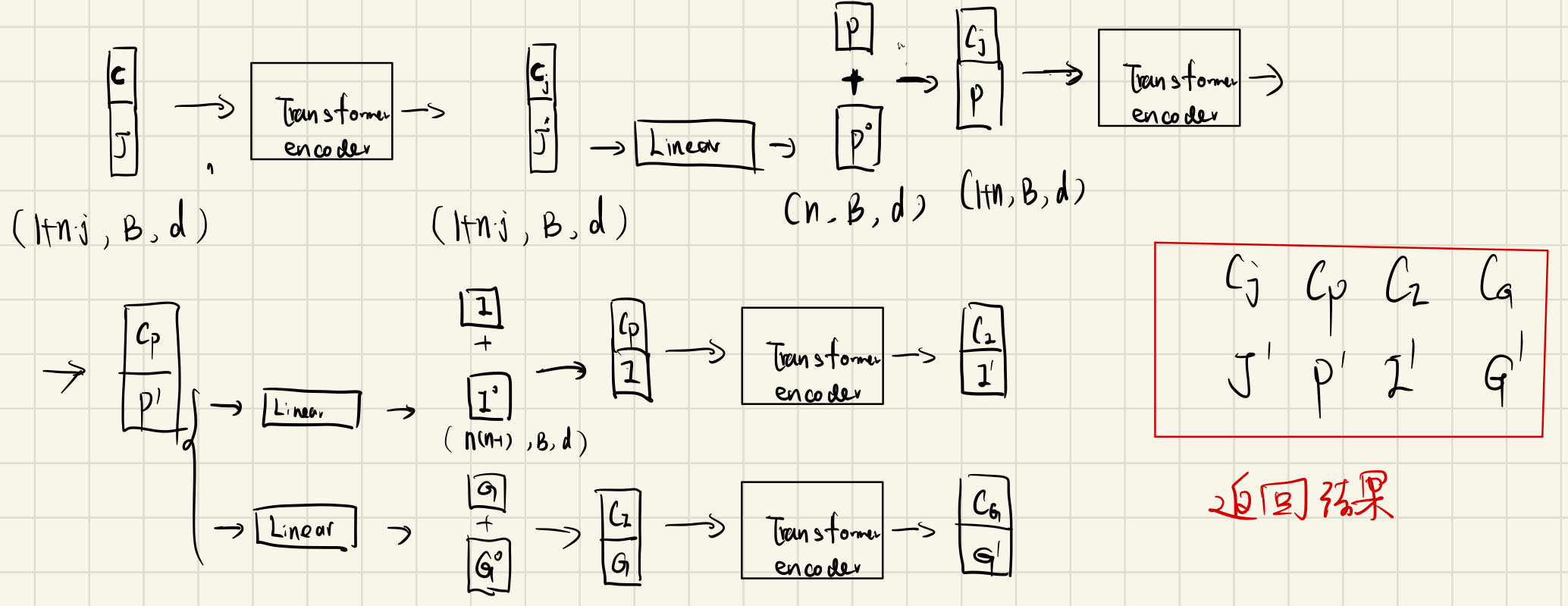
- 下面是我的流程图,整体处理还是比较好理解的:
损失函数计算
1 | # outputs is a list of list |
预测群体logits:
1 | pred_logits = [] |
计算scores:
1 | # fine_cls, middle_cls, coarse_cls, group_cls are from the last layer |
预测个体logits:
1 | pred_logits_person = [] |
loss计算:
1 | # model forward pass |
这部分loss计算挺难理解的,之后看看原文尝试去修改一下
1 | # learning the cluster assignment and computing the loss |
- Post title:代码解构
- Post author:sixwalter
- Create time:2023-05-18 00:00:00
- Post link:https://coelien.github.io/2023/05/18/deep-learning/第一章/代码结构/
- Copyright Notice:All articles in this blog are licensed under BY-NC-SA unless stating additionally.
Comments