Acwing 3305 作物杂交
Content
作物杂交是作物栽培中重要的一步。
已知有 N 种作物 (编号 1 至 N),第 i 种作物从播种到成熟的时间为 Ti。
作物之间两两可以进行杂交,杂交时间取两种中时间较长的一方。
如作物 A 种植时间为 5 天,作物 B 种植时间为 7 天,则 AB 杂交花费的时间为 7 天。
作物杂交会产生固定的作物,新产生的作物仍然属于 N 种作物中的一种。
初始时,拥有其中 M 种作物的种子 (数量无限,可以支持多次杂交)。
同时可以进行多个杂交过程。
求问对于给定的目标种子,最少需要多少天能够得到。
如存在 4 种作物 ABCD,各自的成熟时间为 5 天、7 天、3 天、8 天。
初始拥有 AB 两种作物的种子,目标种子为 D,已知杂交情况为 A×B→C,A×C→D。
则最短的杂交过程为:
第 1 天到第 7 天 (作物 B 的时间),A×B→C。
第 8 天到第 12 天 (作物 A 的时间),A×C→D。
花费 12 天得到作物 D 的种子。
输入的第 1 行包含 4 个整数 N,M,K,T,N 表示作物种类总数 (编号 1 至 N),M 表示初始拥有的作物种子类型数量,K 表示可以杂交的方案数,T 表示目标种子的编号。
第 2 行包含 N 个整数,其中第 i 个整数表示第 i 种作物的种植时间 Ti。
第 3 行包含 M 个整数,分别表示已拥有的种子类型 Kj,Kj 两两不同。
第 4 至 K+3 行,每行包含 3 个整数 A,B,C,表示第 A 类作物和第 B 类作物杂交可以获得第 C 类作物的种子。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 1≤N≤2000,
2≤M≤N,
1≤K≤105,
1≤T≤N,
1≤Ti≤100,
1≤Kj≤M,
|
Output
输出一个整数,表示得到目标种子的最短杂交时间。
Code
initial version of the solution (the following picture is great, there’s no need drawing again)
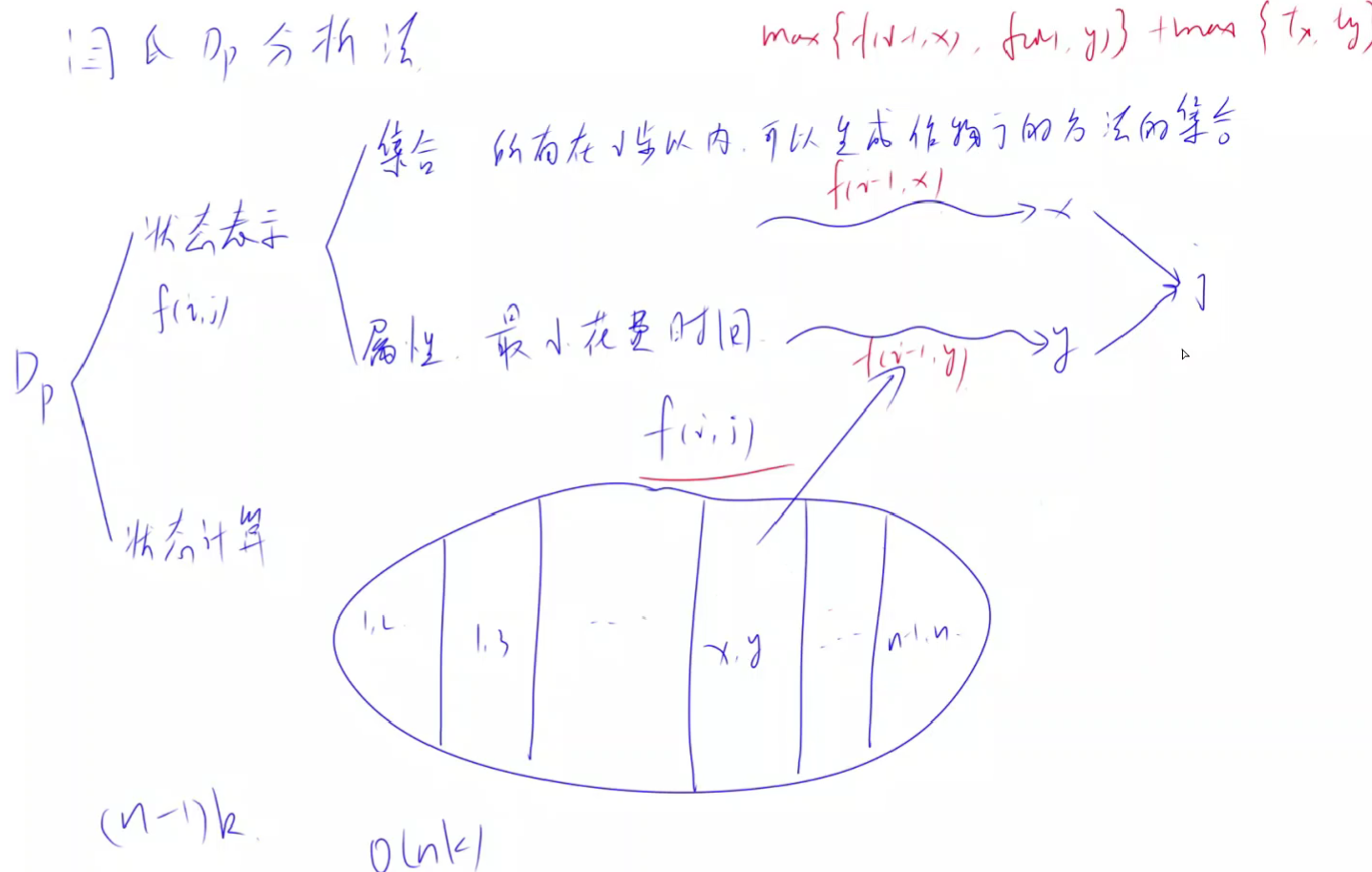
- the first version actually has two dimensions as illustrated by the picture above
- it is essentially a DP solution!
- how to store edges is the key
second version, I optimize the first dimension
Complexity: , where N is the seed number, and M is the Process number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct Process{
int a,b,c;
};
const int N = 2010;
int mature_time[N];
int f[N];
vector<Process> ps;
void bellmanfold(int n){
for(int i=1;i<n;++i){
for(auto pro: ps){
if(max(f[pro.a],f[pro.b])+max(mature_time[pro.a],mature_time[pro.b])<f[pro.c]){
f[pro.c] = max(f[pro.a],f[pro.b])+max(mature_time[pro.a],mature_time[pro.b]);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int n,m,k,t;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
scanf("%d",&mature_time[i]);
}
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof f);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
f[x]=0;
}
for(int i=0;i<k;++i){
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
ps.push_back({a,b,c});
}
bellmanfold(n);
printf("%d\n",f[t]);
return 0;
}
|
Third version, use QUEUE to optimize the solution!
Complexity: normally , worstly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct Process{
int a,b,c;
Process *ne=nullptr;
Process(int a, int b, int c, Process* ne):a(a),b(b),c(c),ne(ne){}
};
const int N = 2010;
int mature_time[N];
int f[N];
Process* ps[N];
queue<int> que;
bool inQue[N];
void insert(int a, int b, int c){
Process * np = new Process(a,b,c,ps[a]);
ps[a] = np;
np = new Process(b,a,c,ps[b]);
ps[b] = np;
}
void spfa(){
while(!que.empty()){
int cu = que.front();
que.pop();
inQue[cu] = false;
for(auto i = ps[cu]; i!=nullptr; i = i->ne){
if(max(f[i->a],f[i->b])+max(mature_time[i->a],mature_time[i->b])<f[i->c]){
f[i->c] = max(f[i->a],f[i->b])+max(mature_time[i->a],mature_time[i->b]);
if(!inQue[i->c]){
que.push(i->c);
inQue[i->c] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int n,m,k,t;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k,&t);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
scanf("%d",&mature_time[i]);
}
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof f);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
f[x]=0;
que.push(x);
}
for(int i=0;i<k;++i){
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
insert(a,b,c);
}
spfa();
printf("%d\n",f[t]);
return 0;
}
|

