
CSAPP笔记:Bits, Bytes and Integer02
Integers
Addition
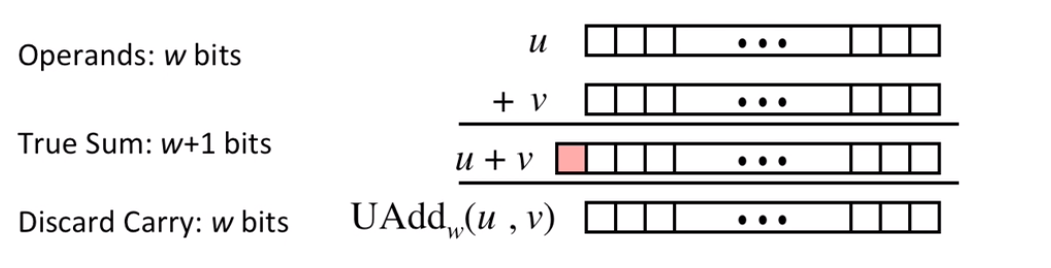
Unsigned Addition
w is the word size(bit)
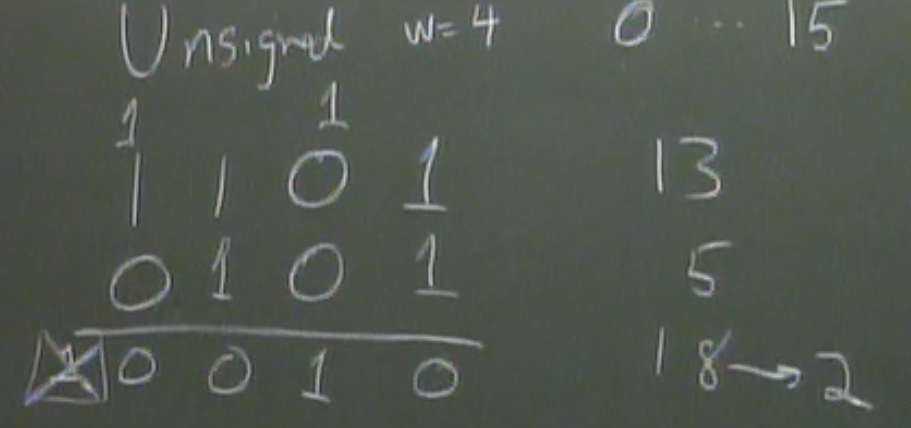
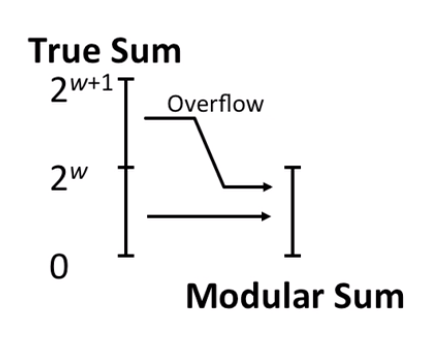
- substract 2^w from the sum
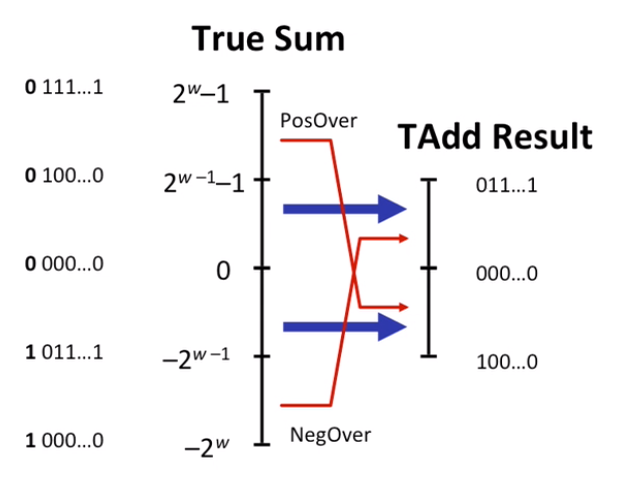
Two’s Complement Addition
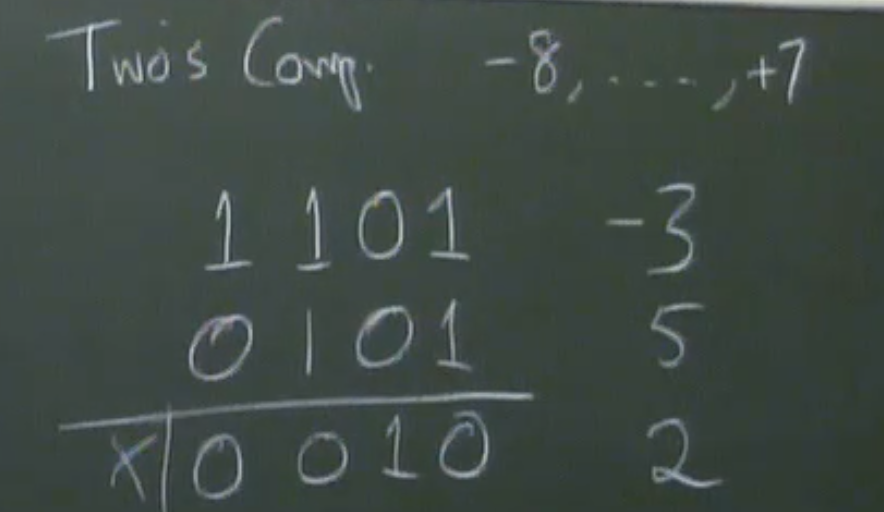
negative overflow
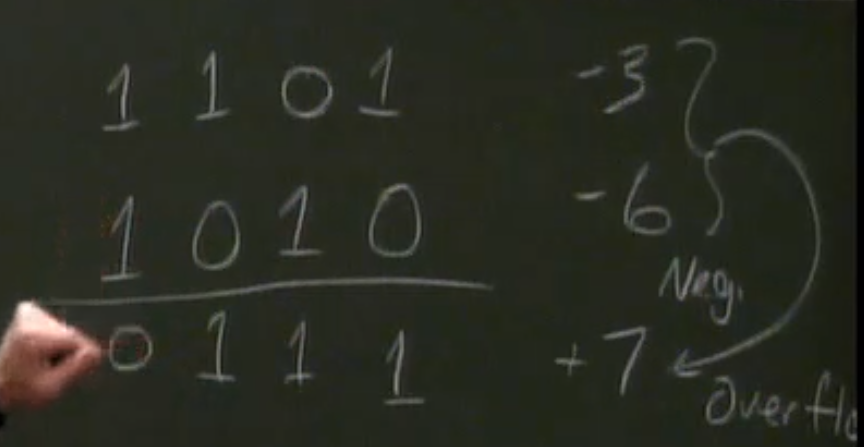
positive overflow
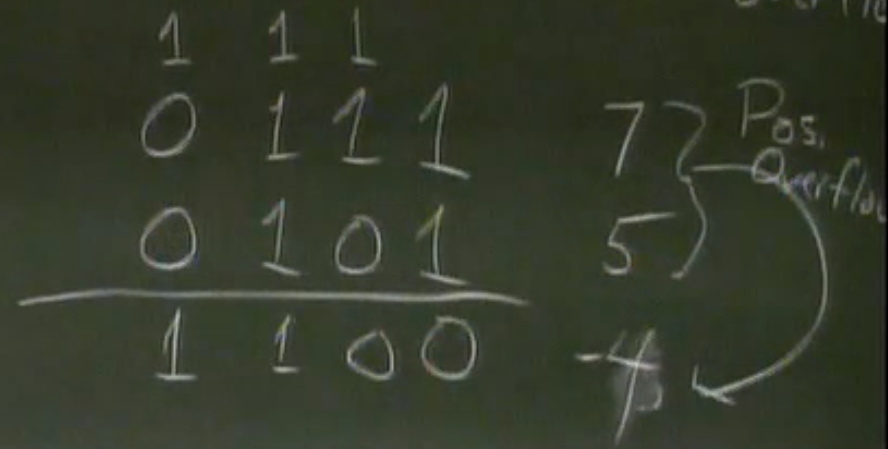
Multiplication
unsigned
signed

Divide with Shift
- round down to zero
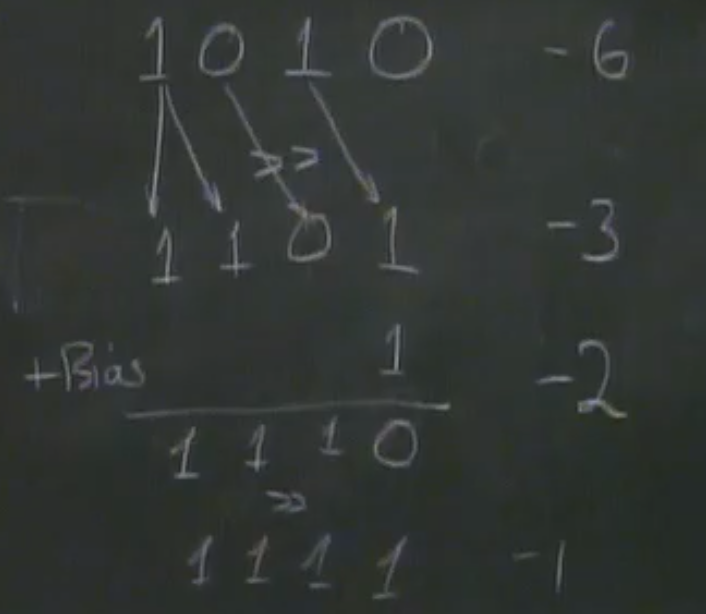
Negative(~ + 1)
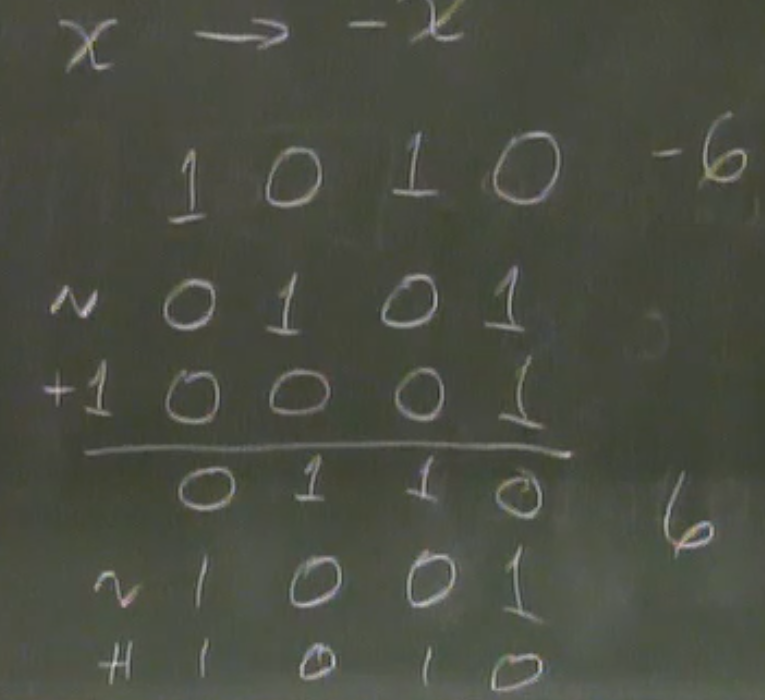
When should use Unsigned?
- when performing modualr arithmetic
- using bits to represent sets
Representations in memory, pointers and strings
Byte-Oriented Memory Organization
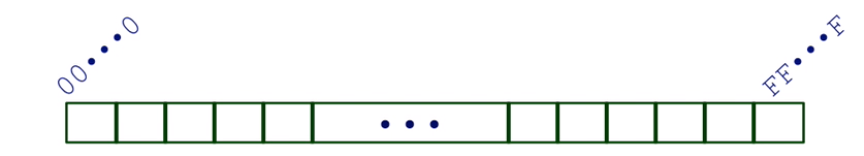
An address is like an index into that array
system provides private address spaces to each “process”
32 bit machines Limits addresses to 4GB
gcc -m {32,64}
Word-Oriented Memory Organization
group bytes to word
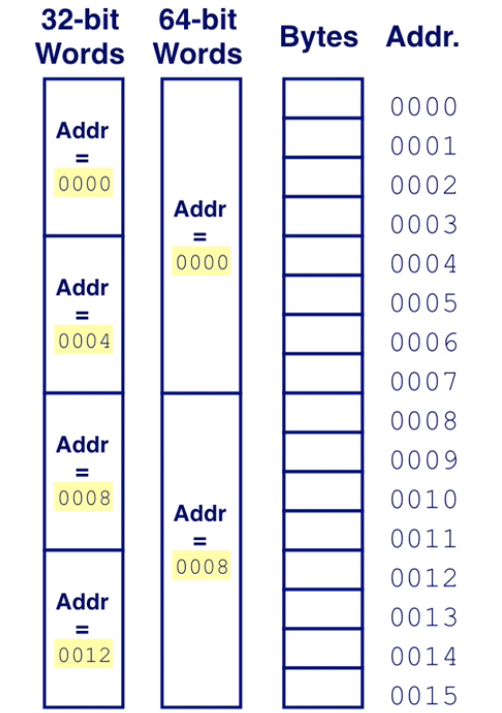
- assume the address of the word is the loweset address of byte in it
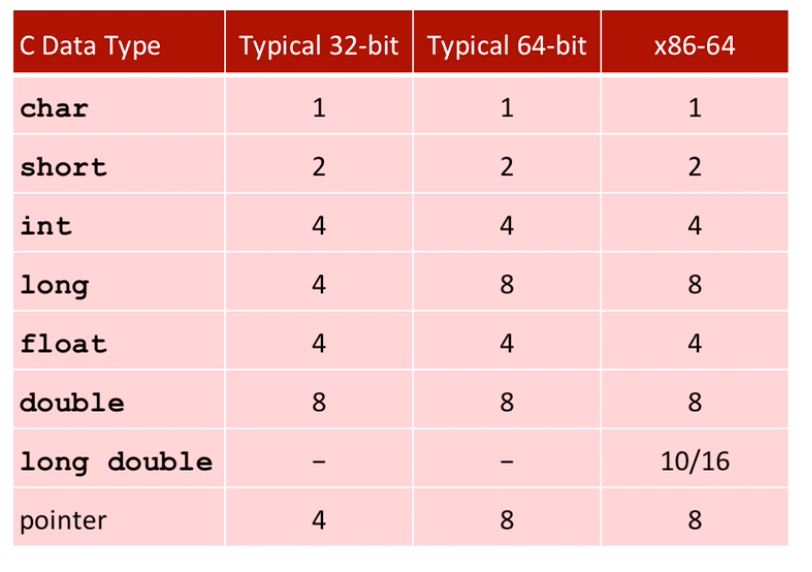
Example Data Representation
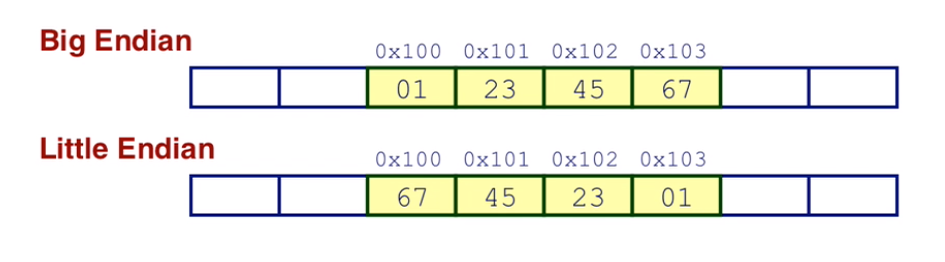
Byte Ordering
how are the bytes within a word ordered in memory?
Big Endian: internet, Sun
least significant byte has highest address
little Endian: x86, Arm, IOS, Windows
least significant byte has lowest address
an example
- Variable x has 4-byte value of 0x01234567
- Address given by &x is 0x100
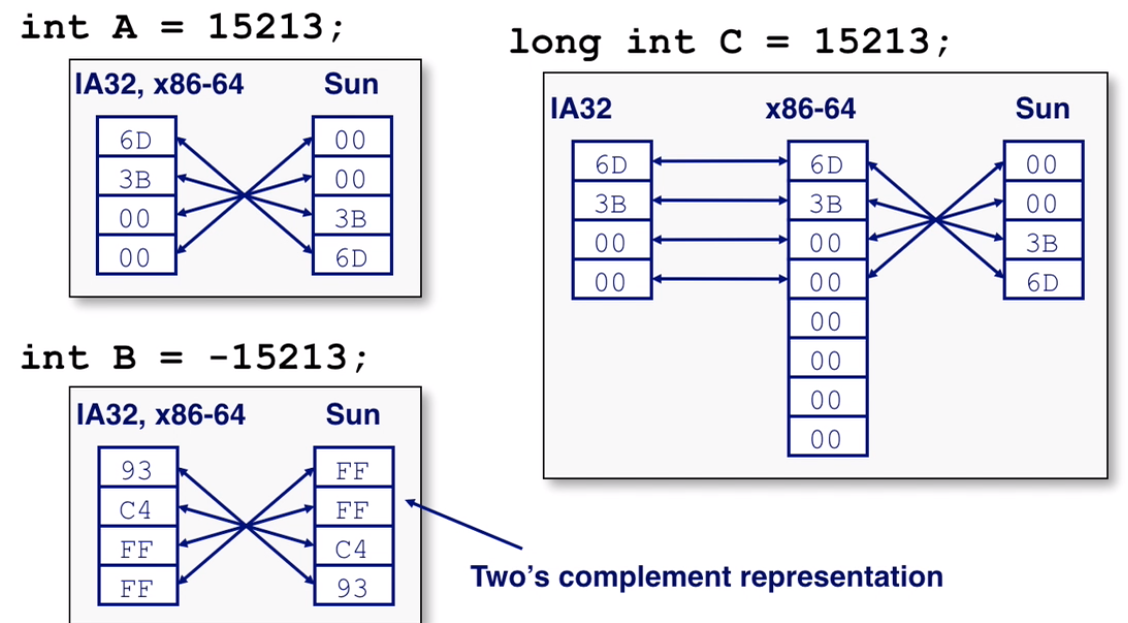
another example
- 15213
- binary: 0011 1011 0110 1101
- hex: 3 B 6 D
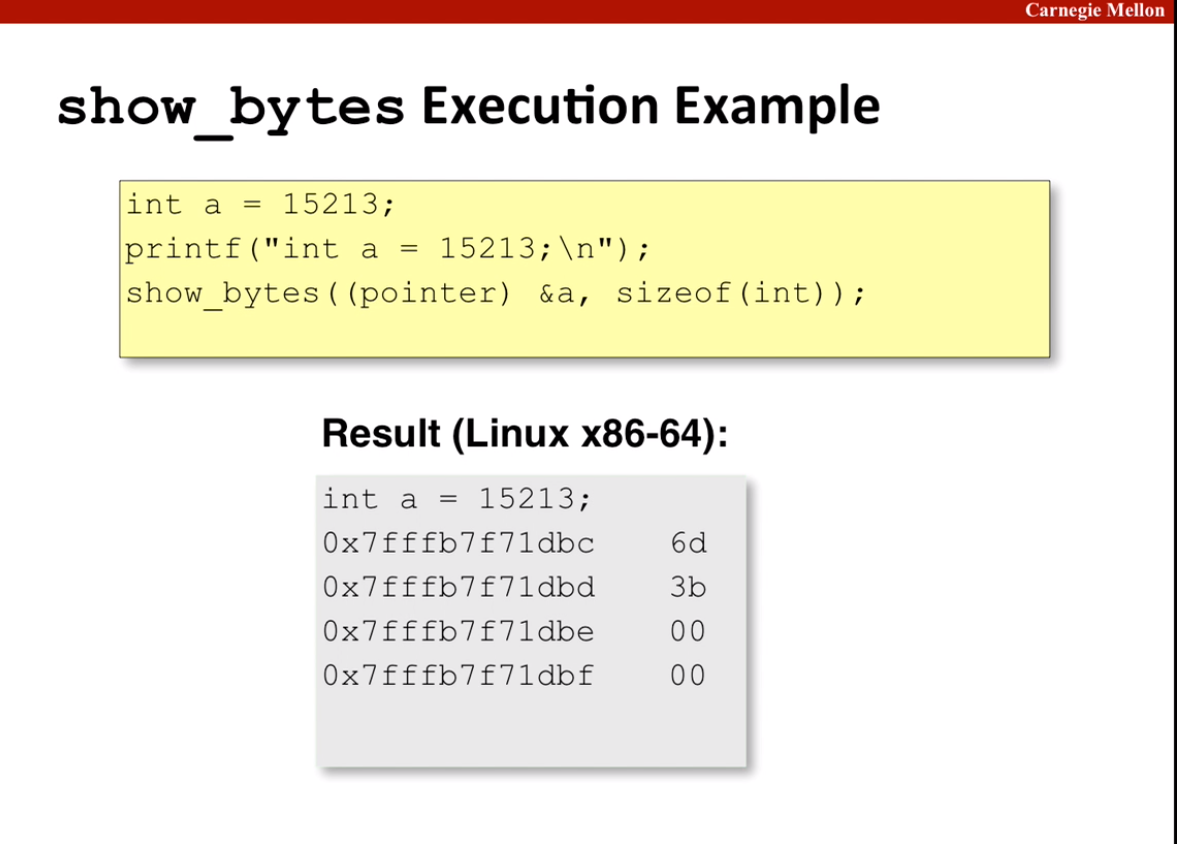
a useful code to print Byte Representation of Data
1 | typedef unsigned char * pointer; |
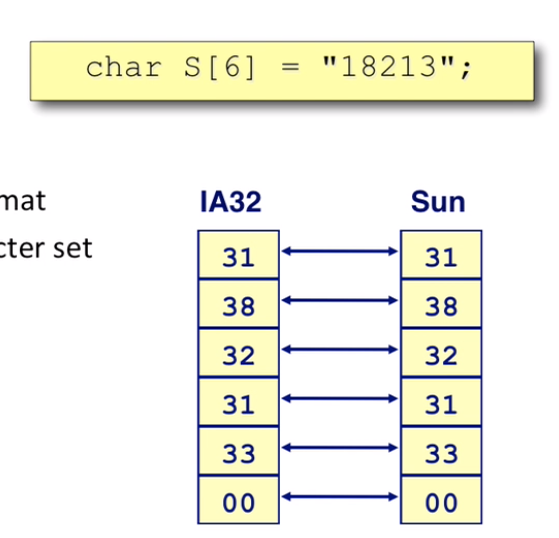
Representing strings
- array of characters
- ASCII format
- null-terminated
Integer C Puzzles
x<0 -> ((x*2)<0)
False Tmin: “100000000” -> “00000000”
ux >= 0
True
x&7 == 7 -> (x<<30) <0
True “1100…000”
ux > -1
never true False
x>y -> -x<-y
False Tmin: -Tmin is still Tmin
x*x >=0
False
x>0 && y>0 -> x+y > 0
False
x >=0 -> -x<=0
True (Tmax)
x <=0 -> -x>=0
False(Tmin)
(x|-x)>>31 == -1
False(0)
- Post title:CSAPP笔记:Bits, Bytes and Integer02
- Post author:sixwalter
- Create time:2023-08-05 11:14:26
- Post link:https://coelien.github.io/2023/08/05/course-learning/CMU-213/213_bits02/
- Copyright Notice:All articles in this blog are licensed under BY-NC-SA unless stating additionally.