CS61A笔记

lecture 01 Course About
managing complexity
- tool: mastering abstraction
- abstraction is giving sth a name and talking about it without worrying about details
- tool: Programming paradigms: about how to organize programs
try a personal project if you have time
lecture 02 Functions
术语
- domain: the set of all inputs
- range: the set of all outputs
- behavior: relationship between input and output
expression evaluate
- all expressions can use function call notation
- evaluate procedure
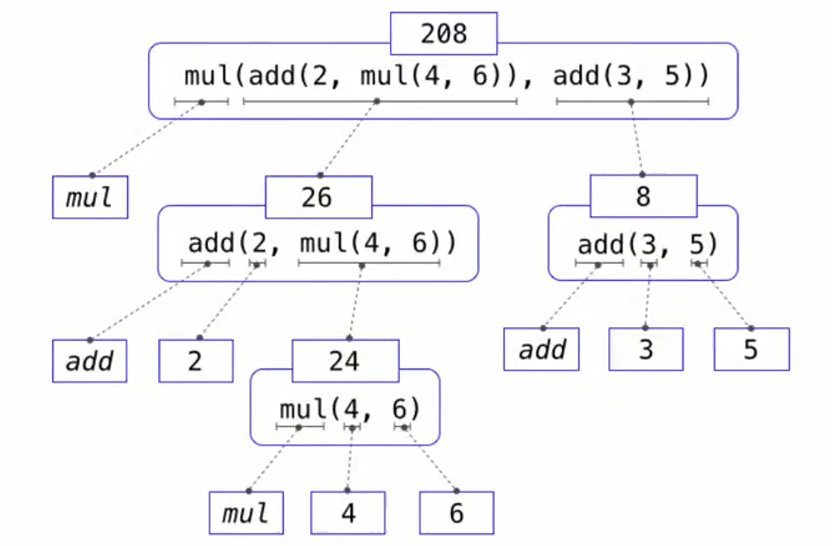
- 上图称为表达式树。add(2,mul(4,6))称为操作数子表达式;其结果称为子表达式的值,同时它也是mul的第一个参数
- 赋值是抽象(abstraction)的最简单的一种方法:把名字绑定到值上
- 函数定义是抽象的一种更强大的手段:把名字绑定到表达式上
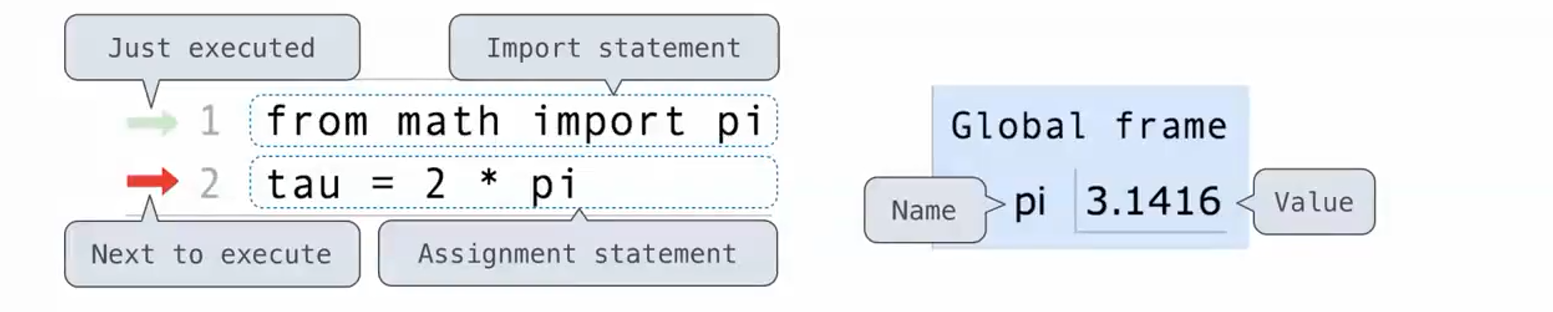
Environment Diagrams
- environment 是 memory, 它可以跟踪名称和值之间的对应关系。
- 所有的表达式都是在environment的情境下计算的。
- envrionment是frames的序列
- 它可以是全局frame,也可以是局部frame,后面跟着全局frame
可视化解释器的执行过程:
函数是如何执行的?
- add a local frame, forming a new environment
- bind the params to its arguments in that frame
- execute the body of the function in that new environment
名称的值是如何查找的?
当前环境下,在最早的frame中找到的名称所对应的值。如在函数中,我们会先在local frame中查找名字,如果没找到,再去全局frame中查找。
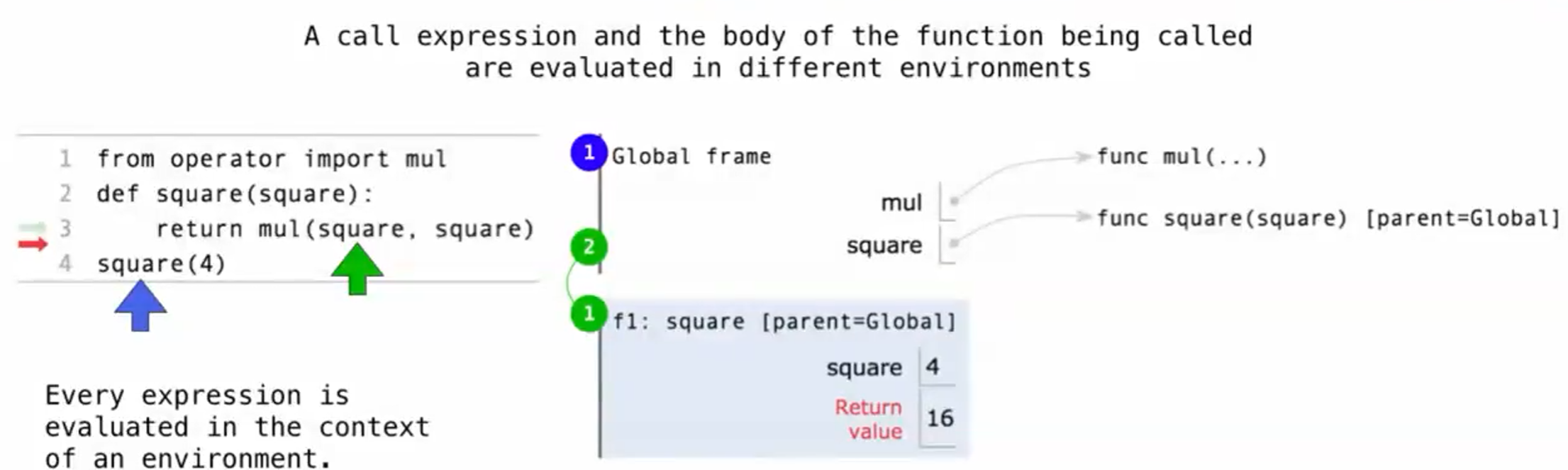
why does it work?
1 | from operator import mul |
函数sqaure在全局frame中,参数square在局部frame中,互不干扰。
lecture 03 Control
print & None
- what happens when evalutate
print(print(1),print(2))?
answer:
1 | 1 |
- use the expression tree:
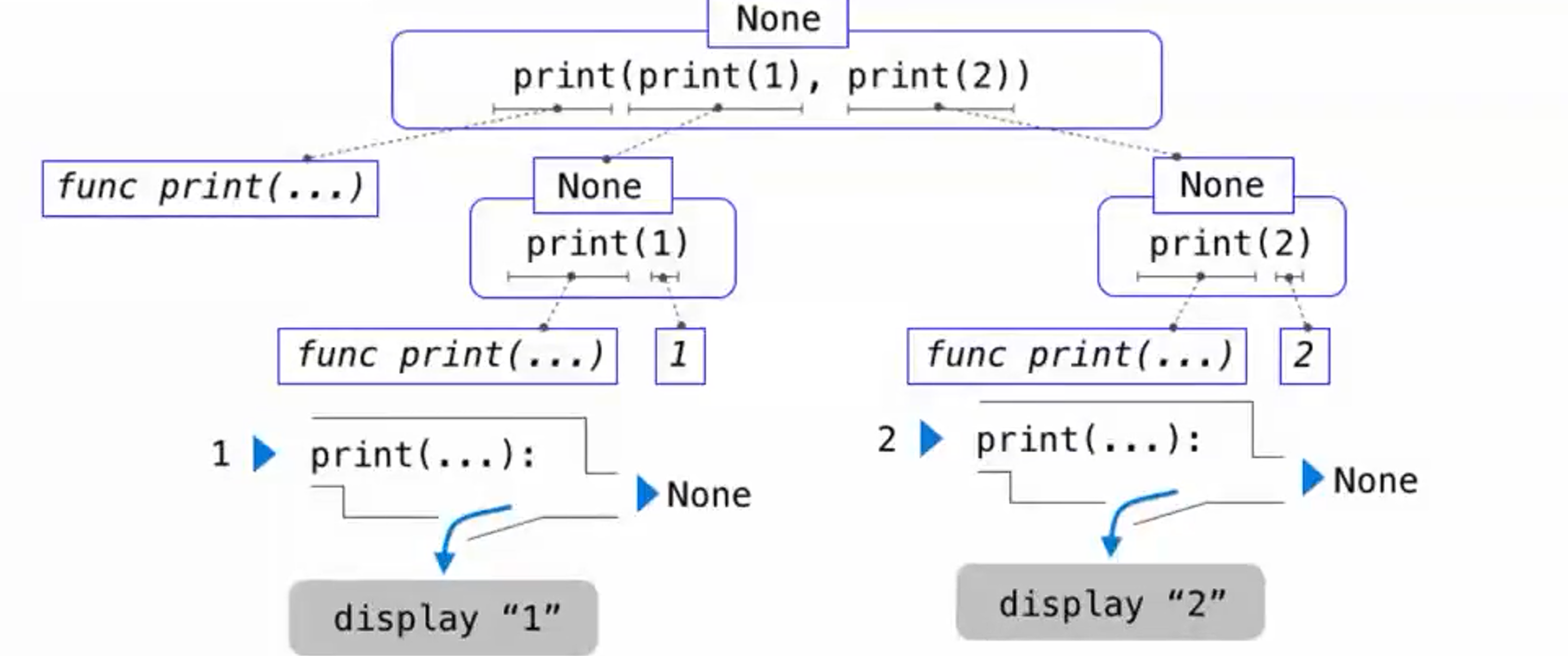
What is None?
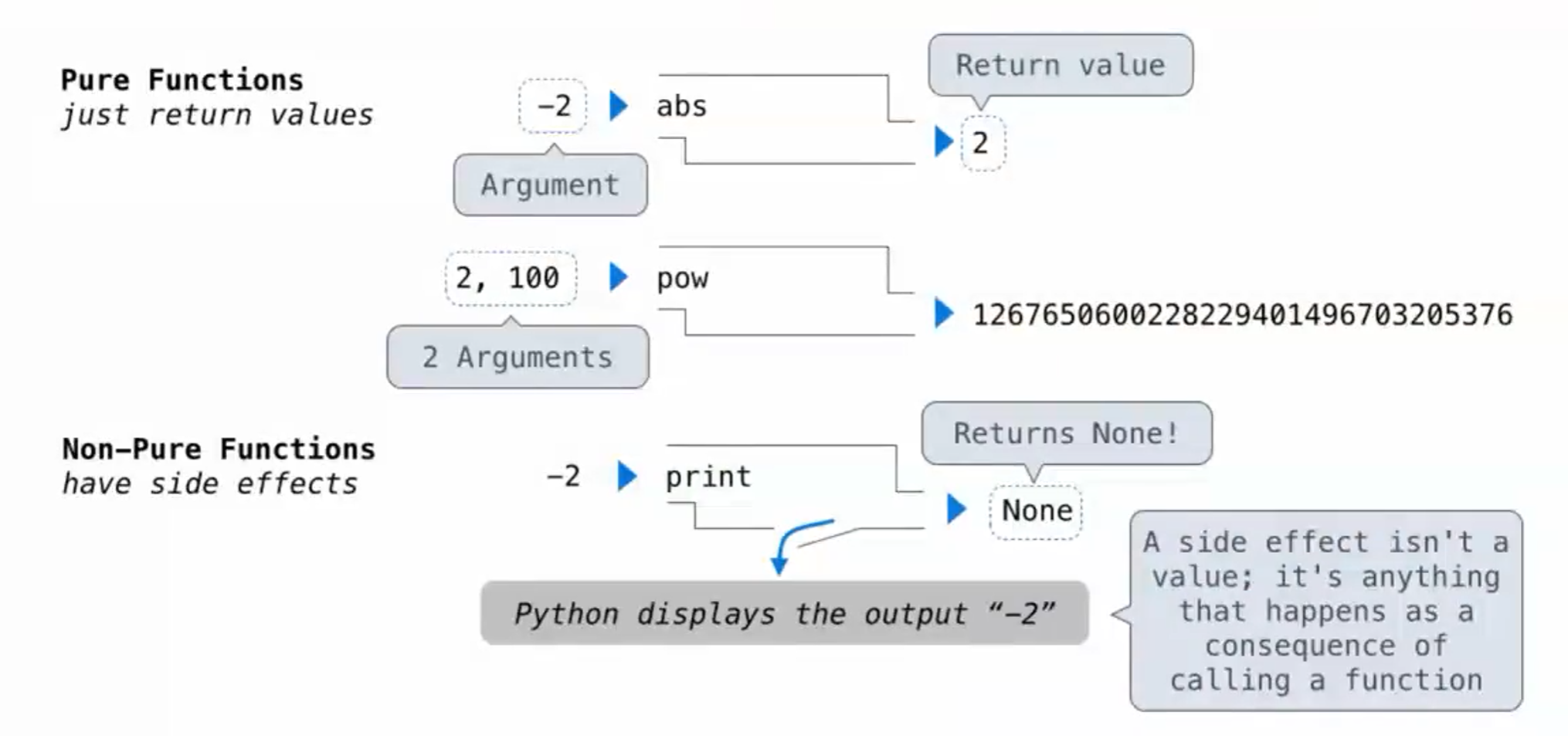
None 表示没有任何东西被返回
None is not displayed by the interpreter as the value of an expression
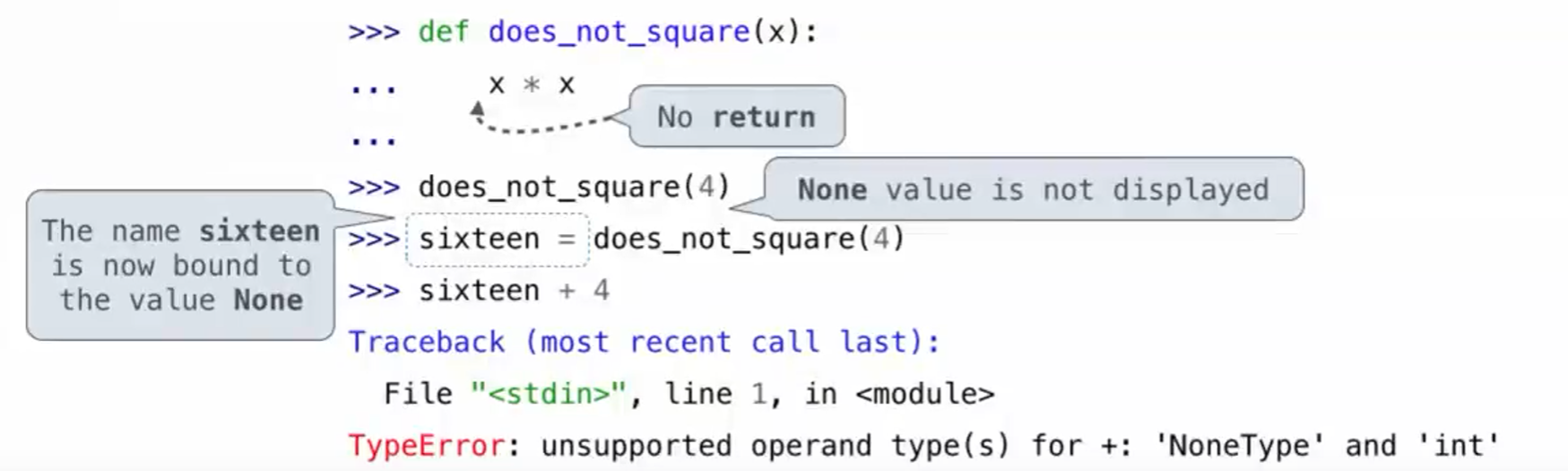
纯函数&非纯函数
- 纯函数:单纯地返回值
- 非纯函数:有些side effects。例如 print,它返回None,但同时会输出值
Multiple Environments in One Diagram
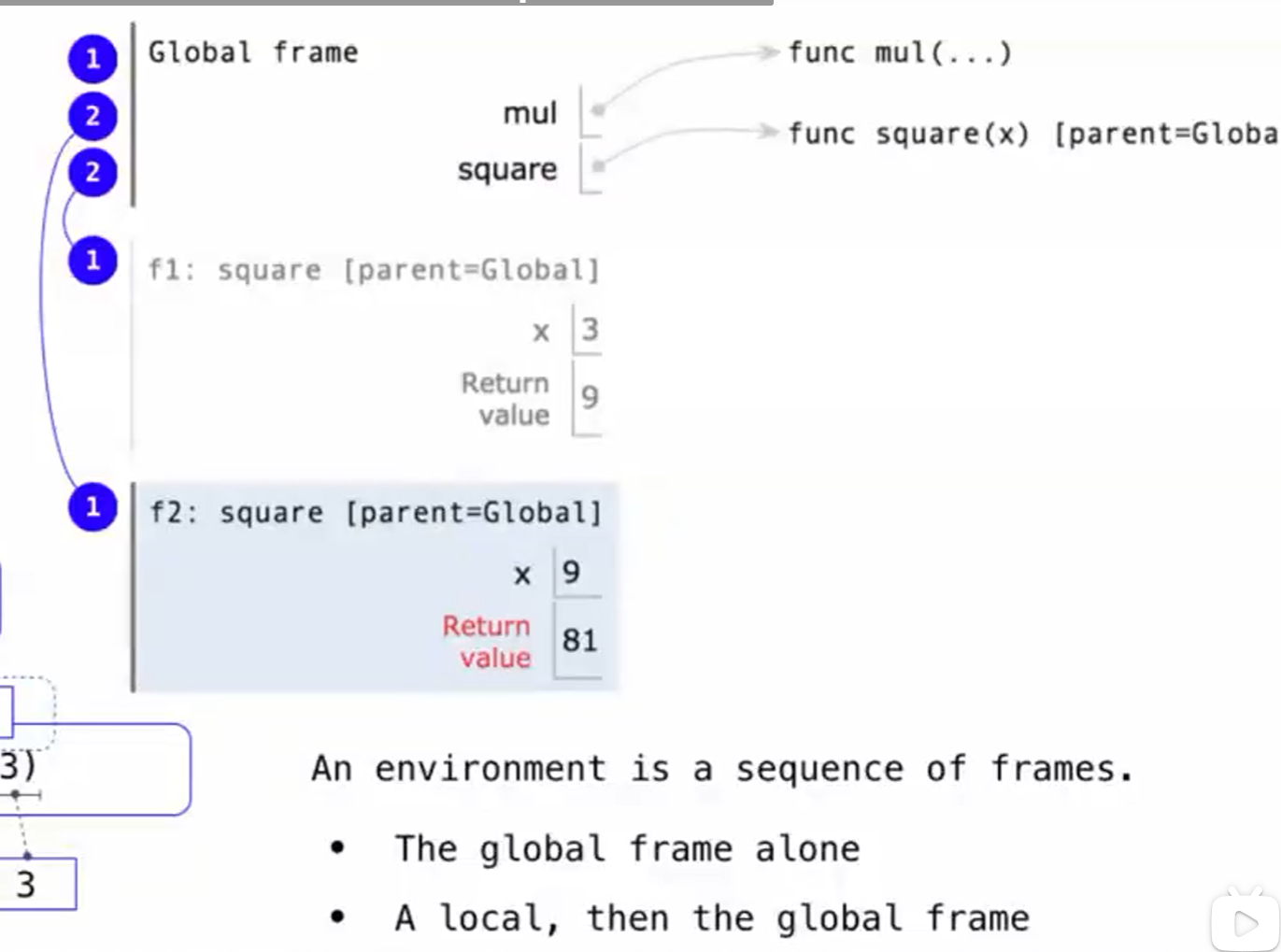
- As you can see, there are three environments as the program executes.
- 失去了环境,名称将不再有意义。名称在不同的环境中有着不同的含义
lecture 04 High Order Functions
A guide to design functions
- Give each function exactly one job
- Don’t repeat yourself. Implement a process just once
- Define functions generally (share implementation)
Generalizing patterns with arguments
Generalizing Over Computational Processes
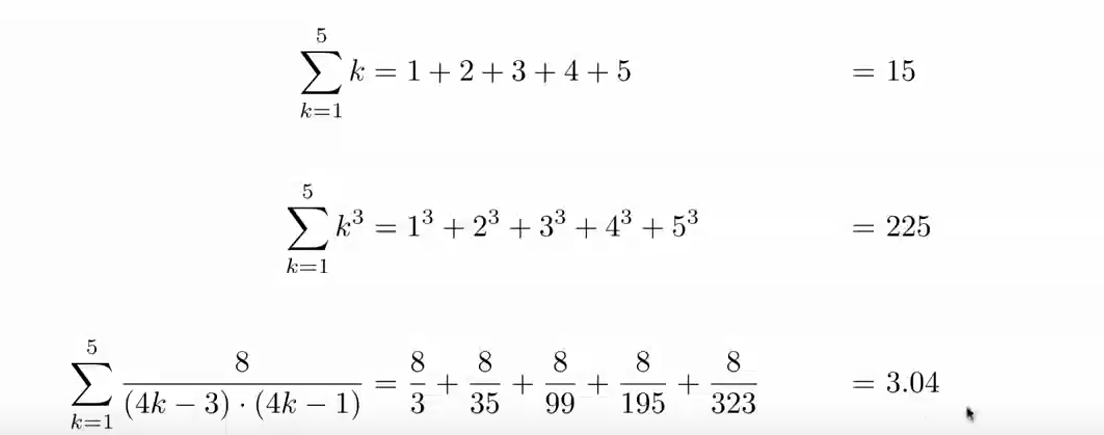
- all summing from 1 to 5
- how to generalize?
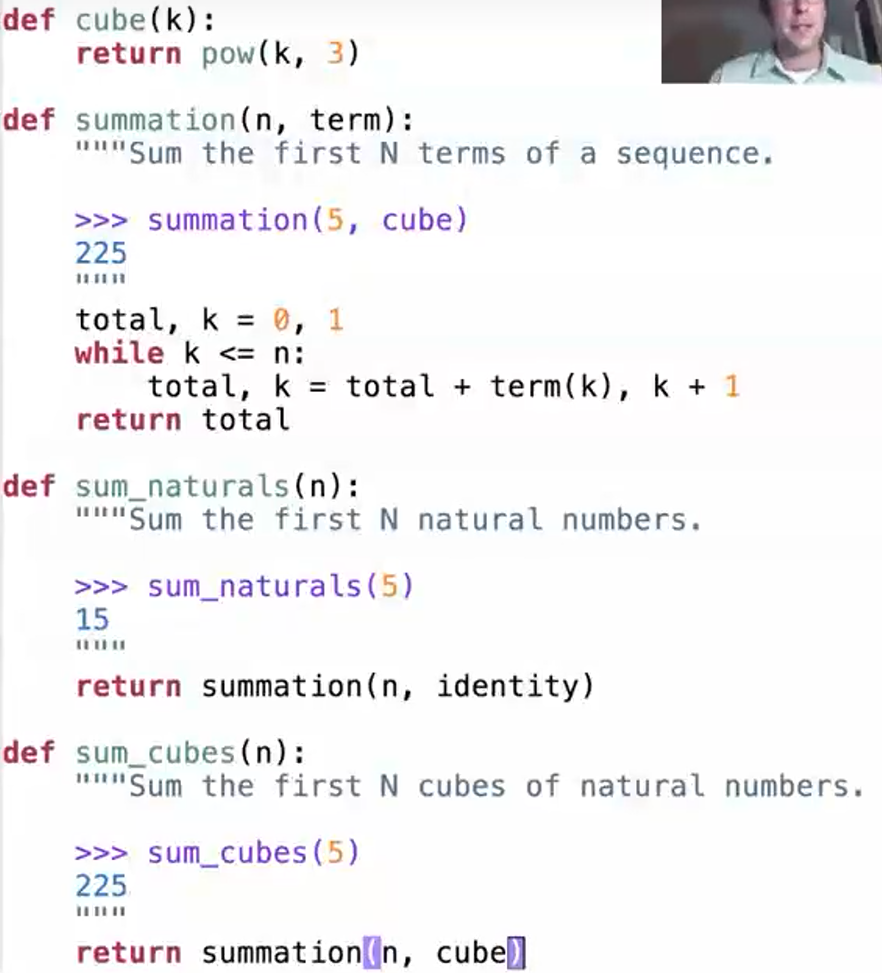
- term is a formal parameter which will be bound to a function
- so the summation is a high order function that take another function as an argument
Functions as return values
- function can be manipulated as values in programming
- high order function
- take another function as an argument
- return a function
- Post title:CS61A笔记
- Post author:sixwalter
- Create time:2023-08-05 11:14:26
- Post link:https://coelien.github.io/2023/08/05/course-learning/CS-61A/note01/
- Copyright Notice:All articles in this blog are licensed under BY-NC-SA unless stating additionally.
Comments