MIT6.S081笔记:lecture 3

MIT6.S081笔记:lecture 3
OS design
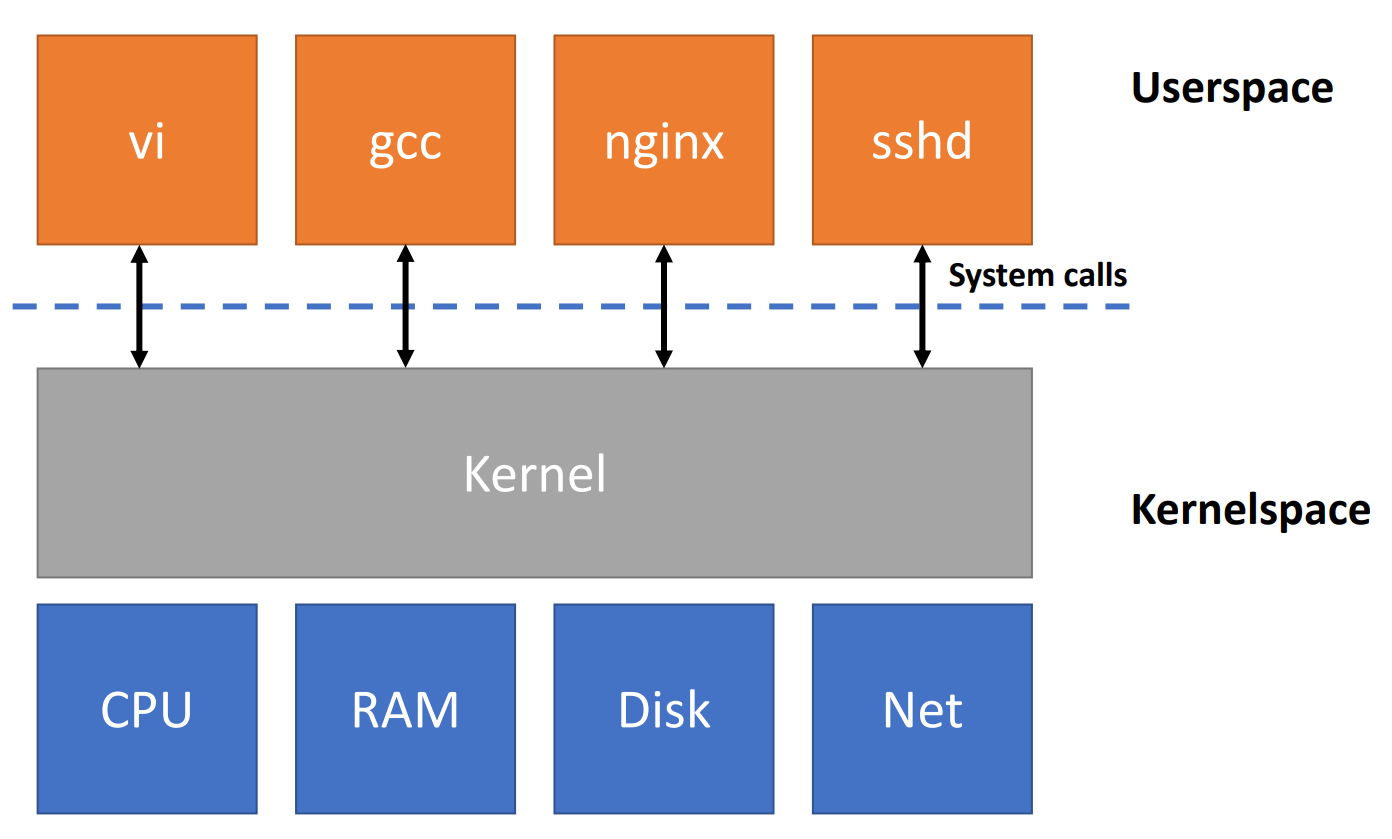
OS organization
Strawman design: NO OS
Application interact directly with the OS:

OS acts as a library:
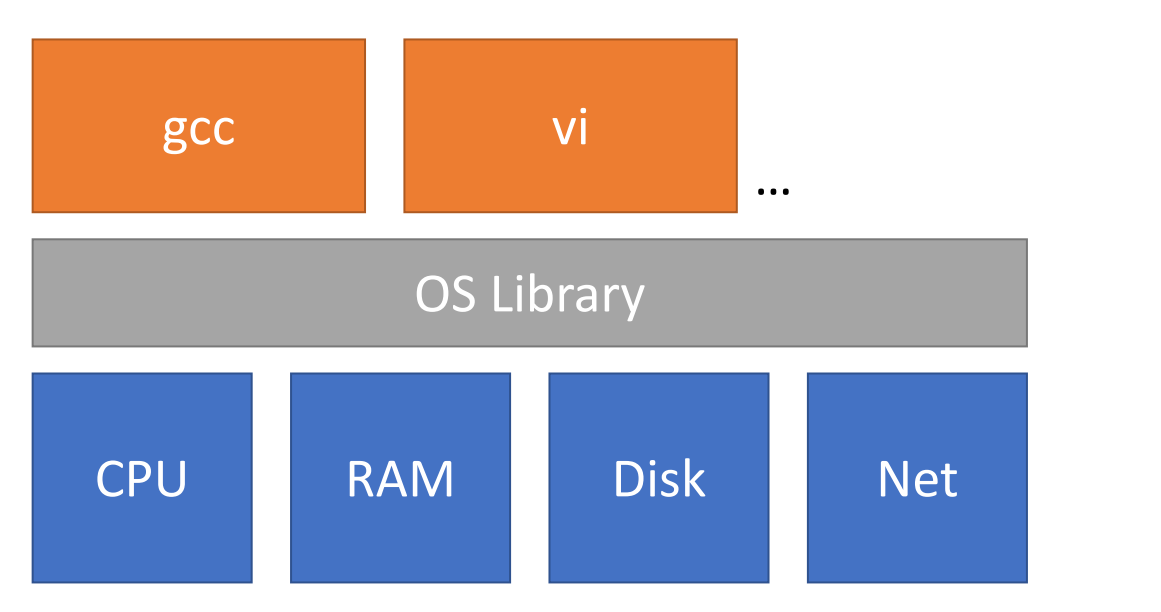
which is not a good design, because it doesn’t have enforced multiplexing and strong memory isolation
Unix interface
- abstract the hardware resources to provide strong isolation
- processes: instead CPU: fork()
- OS transparently allocates cores
- enforce that processes give them up
- memory: instead physical memory: exec(), brk()
- Each process has its own memory
- OS decides where to place app in memory
- OS enforces isolation between apps
- OS stores image in file system (loaded with exec)
- files: instead disk block: open(), read(), write()
- OS provides convenient names
- OS allows files to be shared by apps and users
- Pipes: instead shared physical memory: pipe()
- OS buffers data
- OS stops sender if it transmits too fast
OS should be defensive
- app can not crash the operating system
- app can not break out of its isolation
- it means Strong Isolation between apps and OS
- hardware support
- user/kernel mode
- virtual memory
- hardware support
User/Kernel mode
- kernel mode: privileged instructions
- changing back to user mode
- programming a timer chip
- controlling the virtual memory
- user mode: unprivileged instructions
CPU provide virtual memory
page table
map virtual addr to physical addr
defines what physical memory an app can access
process has its own page table
System calls
- apps need to communicate with kernel
- solutions add instruction to change mode in controlled way:
- ecall
- enter kernel at pre-agreed instruction address
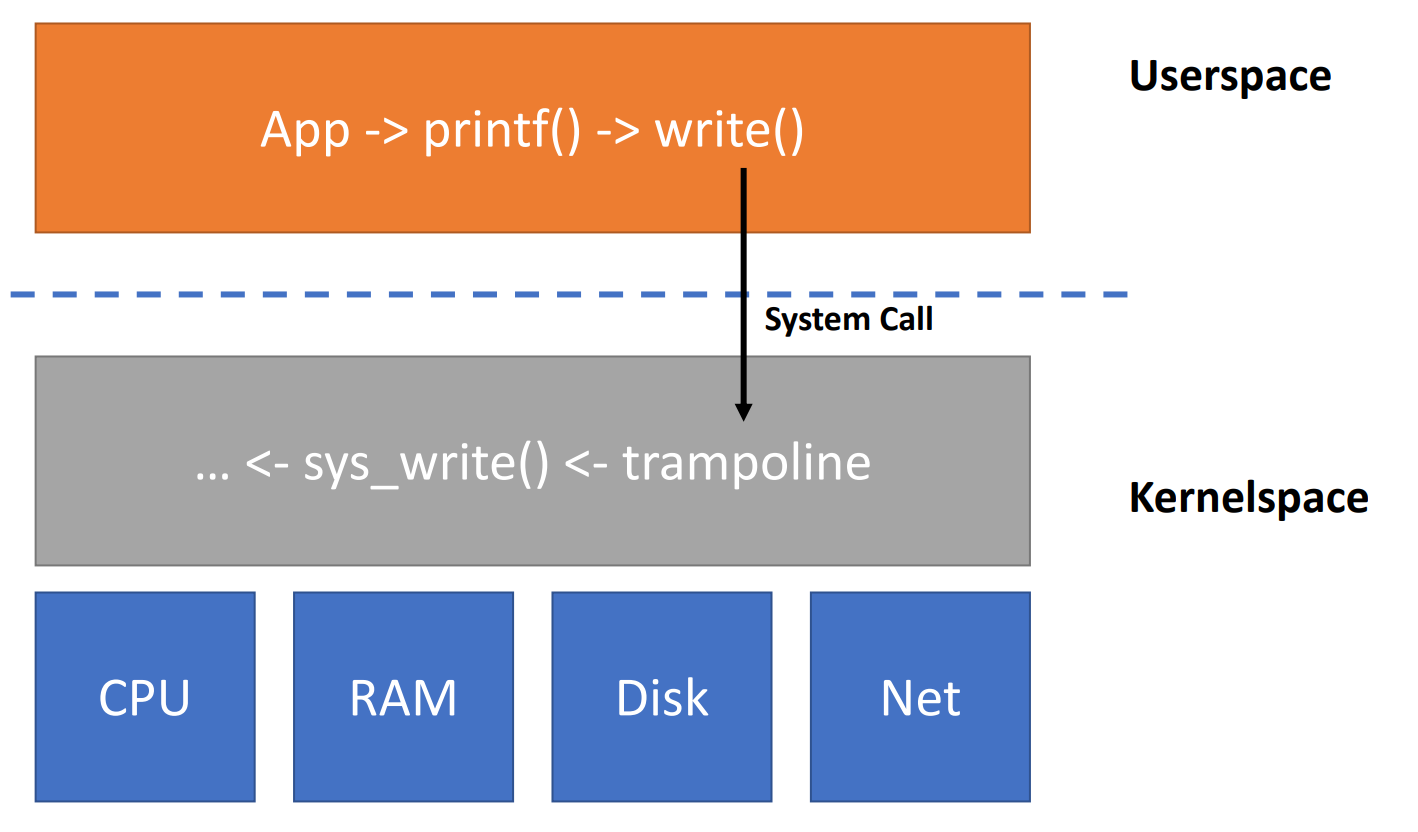
Entering the kernel
ecall
- fork();
- ecall sys_fork -> syscall
- write()
- ecall sys_write -> syscall
Trusted computing base
kernel must have no bugs
kernel must treat process as malicious
security mindset
Monolithic kernels
- kernel is one big program with everything
- Kernel interface == system call interface
- Pros:
- good performance
- easy for subsystems to cooperate
- cons:
- Interactions are complex
- No isolation within
Microkernels
- Runs OS services as ordinary user programs
- kernel implements minimal mechanism to run services in user space
- IPC
- process with memory
- Kernel interface != system call interface
- Pro:
- more isolation
- easy to debug
- Con:
- Hard to get good performance
- complexity
- Post title:MIT6.S081笔记:lecture 3
- Post author:sixwalter
- Create time:2023-08-05 11:14:26
- Post link:https://coelien.github.io/2023/08/05/course-learning/MIT6.S081/lec3/
- Copyright Notice:All articles in this blog are licensed under BY-NC-SA unless stating additionally.
Comments